
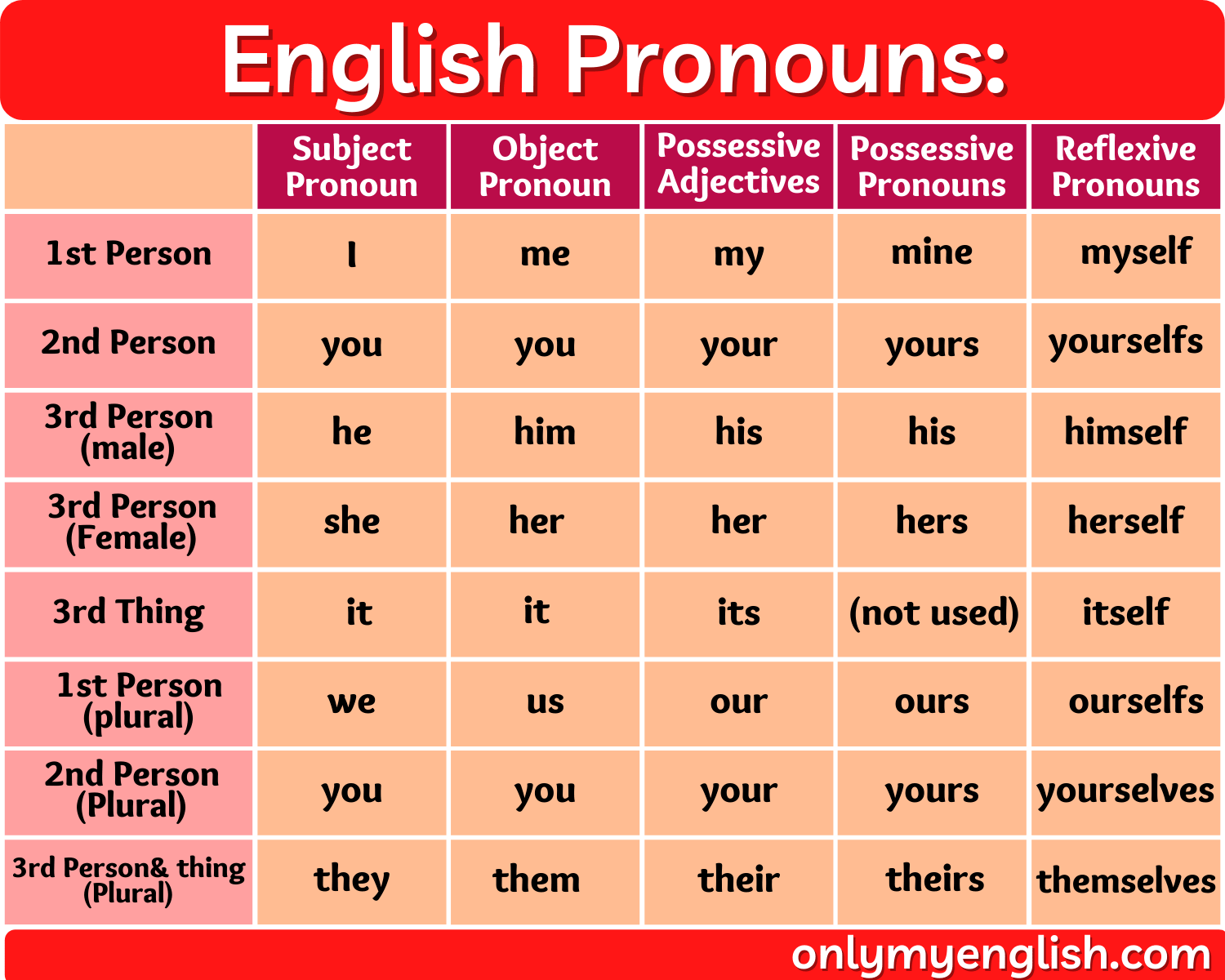
Words within the category are himself, herself, themselves, yourself/ves, myself, itself. The reflexive pronoun will end in -self or -selves and is used in reference to another pronoun. Object pronoun list: me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them.Įxamples of object pronouns in sentences: Object pronouns are used when the person or thing is the object of the sentence. Subject pronoun list: I, you, he, she, it, we, they. When the person or thing is the subject of the sentence, subject pronouns are used. There are two types of personal pronouns: subject and object. This type of pronoun is used to refer to a person, in this category you will see words such as I, we, you, they, he, she, … We will now take a look at each of these. Most often, pronouns fall into one of nine categories. We briefly discussed some of the different words that are classed as pronouns, however there are also different types of pronouns. I love it! My beautiful yellow jacket makes me happy.Įnglish Pronouns can be divided into several categories: personal, indefinite, reflexive, reciprocal, possessive, demonstrative, interrogative, reciprocal and relative.Most people choose not to do this because it can confuse the reader. Technically, you can place a pronoun before an antecedent. If you know who is speaking, the pronouns I, me, and you can be clearly understood. If the context of a sentence remains clear an antecedent is not necessary. Sometimes a writer will not explicitly need to include an antecedent. The sun smiled while it ducked under the clouds.Mary decided that she would drive down to visit her grandmother.You will find the antecedents in the examples below italicized. For example, it can refer to many different nouns: a garden hose, a shed, or almost any other noun you may need to mention. The antecedent allows readers to know what a particular pronoun is referencing. AntecedentĪn antecedent, a noun or noun phrase, provides context for a pronoun. Using she and her makes it clear that Mary is being referenced. Mary went to the store to buy a shirt. She picked up a blue shirt to go with her jacket.For this reason, we use pronouns for noun substitutions. The reader may think that the two names you use are different entities entirely.

You could use alternative appellations to make the text more varied. Mary picked up a blue shirt to go with Mary’s jacket. Mary went to the store to buy a shirt.For example, if we wanted to write a story about Mary we would constantly have to repeat her name. Without pronouns, we would have to constantly repeat the same noun over and over again to tell a story. A pronoun is a word that substitutes for a noun or noun phrase. One of the nine parts of speech in the English language is the pronoun. Choosing a singular pronoun for a plural noun.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
